Symphysis pubic dysfunction described as pain and discomfort in the pelvic & groin area caused by a misalignment or stiffness of the pubic joint. It happens when the ligaments that keep pubic bone & pelvis stable become overstretched, lax & no longer stabilize the pelvis. It can cause extreme pain around the pelvic area & can extend down into the groin & mid-thigh. It is most common in pregnant women but it can be developed in men & women that have previously had a fall or damage to the pelvic. It affects approximately one out of five pregnant women. It is painful & can have a significant impact on patient mobility & patient quality of life which can lead to potentially serious problems. It usually worsens when the person is active. It is not life-threatening but it can be life-limiting.
Symphysis Pubic Dysfunction Anatomy
The pubic symphysis is a non-synovial amphiarthrodial joint between the pelvic bones at the front of the pelvis connected by a small fibrocartilaginous disc. The fibrocartilaginous disc is reinforced by a network of ligaments. It is normally a very rigid joint at which very little movements occur. It may contain a fluid-filled cavity. The center of the pubic symphysis is avascular. Both pubic bones are covered by a thin layer of hyaline cartilage. The symphysis pubis is 9-10 mm in width with thick cartilaginous endplates during birth. The adult size is achieved during mid-adolescence. The end plates decrease in width to a thinner layer during adulthood. Dysfunction occurs when this pubic joint becomes too lax.
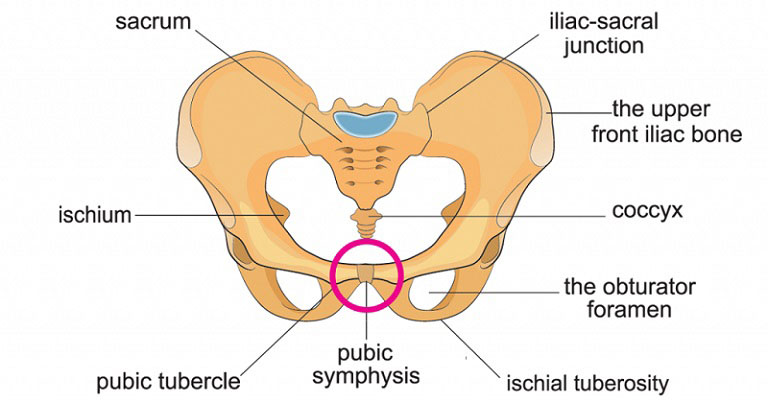
Symphysis Pubic Dysfunction Causes
The exact cause is still unknown. But it is believed to be due to excessive or repetitive stress to the pubic symphysis. There are certain conditions that can predispose to symphysis pubic dysfunction.
Pregnancy
There are two hormones that are produced during the early pregnancy period. Relaxin and progesterone are responsible for breaking down collagen in the ligaments. It causes laxity & softening of the ligaments. As a result, increased joint mobility. It is most worse in the last trimester of pregnancy. It can be aggravated if pregnant women performing strenuous activities.
During pregnancy, there is an altered load on the pelvis which can lead to spino – pelvic instability.
Sports Injury or Trauma
Anyone playing sports can suffer symphysis pubic dysfunction due to –
- Overuse of hip adductor & gracilis muscle
- Overloading forces on the pelvis
- Overstretching or rupture on pelvic musculature
- Biomechanical issues – muscle weakness, poor posture, excessive weight gain & underlying joint hypermobility or hypermobility syndrome.
- Anatomical/genetic pelvic variation
- Alternations in pelvic stability & function
- Previous history of low back pain or pelvic injury.
- Physical strenuous daily activities.
- Obesity before pregnancy.
- Maternal hip dysplasia.
- Direct major or minor trauma of pelvis from a car accident, fall, childbirth.
- Previous difficulty deliveries.
- Ankylosing spondylitis.
- History of bladder or prostate surgery.
- Stiffness or loss of motion of the hip.
Symphysis Pubic Dysfunction Risk Factors
There are certain factors which increase the risk of symphysis pubic dysfunction :
- Experiencing pelvic pain in a previous pregnancy.
- Having an injury to the pelvis.
- Previous pelvic or back pathology or trauma.
- Lack of regular physical exercise.
- Postpartum breastfeeding.
- Rheumatological disorder.
- Macrosomia.
- Tightness of muscles.
- Weak adductor strength.
- Forces that occur during sports such as kicking, acceleration & deceleration.
- Limited internal hip rotation.
- Sacroiliac joint fixation.
- Lower limb biomechanical abnormalities.
- An elevated BMI (Basal metabolic rate)
Symphysis Pubic Dysfunction Symptoms
The severity of symptoms of symphysis pubic dysfunction may range from mild discomfort to severely debilitating pain. Symptoms of symphysis pubic dysfunction are –
- The most common symptom is a sharp pain in the pelvic area that includes the front of the pubic bone & lower side.
- Shooting or aching pain felt in the lower pelvis area.
- Reduce & difficulty of mobility due to the pain.
- Sometimes the presence of pain felt in the perineum area or over the coccyx.
- A clicking or popping or grating sound in the pelvis.
- Waddling walking gait is adopted.
- A gap is palpable in the pubic symphysis.
- Tenderness to palpation of the pubic symphysis.
- Hip joint pain.
- Sacro – iliac joint pain.
- Pain worsened with stretching activities.
- Suprapubic edema & swelling present.
- Pain in a prolonged sitting position.
- Pain relief when resting.
- Pain is exacerbated during walking, climbing stairs, or getting out of bed, single-leg stance.
- Decreased unilateral hip range of motion.
- Urinary incontinence in rare cases.
- Weakness when bending the hip or kicking.
Symphysis Pubic Dysfunction Diagnosis
Symphysis pubic dysfunction is diagnosed by a combination of patient descriptive symptoms & a series of tests designed to look at the stability, movements, pain in the structure surrounding the pelvic joints. Early diagnosis, patients have much less pain & improve more quickly. There are following methods are using for diagnosis of pubic symphysis dysfunction –
- Physical examination – it is done by health professionals to rule out other lumbar spine problems. Physical examination shows tenderness to palpation directly over the pubic symphysis.
- Imaging – It is the only way to confirm the diagnostic tool for pubic symphysis dysfunction. It’s also a useful tool for monitoring the progress of pubic symphysis dysfunction. There are many imaging tests such as X-ray, CT scan, ultrasonography, MRI may help the physician confirm a diagnosis of pubic symphysis dysfunction. Plain radiographs are used to assess vertical mobility. Computed Tomography (CT), Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) & ultrasound scans are used to assess the misalignment of pelvic bones.
X-rays
It is a useful measurement tool for the diagnosis of pelvic instability. Pubic symphysis dysfunction are frequently identified by x-ray (single leg & flamingo stress type).
- Physician detects soft tissue calcification & assesses premature degenerative change in pubic symphysis by single-leg x-ray. It is a simple, inexpensive, diagnostic tool.
- Physician measured the amount of vertical displacement of pubic symphysis by Flamingo stress types x-ray. It also helps to assess passive ligamentous stability.
High-Resolution Ultrasound
It is a simple, safe tool for assessing symphyseal widening in pregnancy & the puerperium. It may also help to rule out other conditions. Transvaginal or trans-perineal types of ultrasonography are used to measure the interpubic distance. It also uses to detect para – symphysial tendonitis, abnormal pubic symphysis & changes of pubic apophysitis.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
It is used to detect disco capsular tear in pubic symphysis & para symphysial tendonitis. It also helps to detect any bony changes, joint irregularity & fluid imbalance in the joint.
Isotope Bone Scan
It is used to assist the exclusion of other musculoskeletal causes of groin pain. It also helps to assess poor test sensitivity of pubic symphysis. For detecting increased radiotracer uptake in pubic symphysis, it also performed.
Symphysis Pubic Dysfunction Treatment
In severe cases where extreme pain is present & the patient can’t be able to move around easily & dressing difficulty also present, the patient needs to consult with his / her physician as soon as possible.
Medication
Over-the-counter drug & pain relievers medications help to ease the symptoms of pubic symphysis dysfunction. It is advisable to discuss with a physician about pain relief medications. NSAID is used to relieve pain, but it is not usually advisable to take NSAID in pregnancy. Take an anti-inflammatory medicine such as ibuprofen or other medicine for pain relief. Consider local corticosteroid injection in acute cases.
Physical Therapy Management of SPD
In most cases of SPD, physical therapy is the first course of treatment. The aim of physical therapy is to minimize pain, improve muscle function, improve pelvic joint position & stability. Physical therapists use different types of modalities to increase, restore mobility & help return patients to their pre-injury level of activity. Physical therapy may include –
- Electrotherapy – Various types of modalities are used to relieve pain. e.g. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS).
- Manual therapy – different types of hands-on treatment are given to the muscles & joints for gently mobilize or move the joints to get them back into position & help them move normally again. It can also help to correct stiffness or imbalance.
- Exercises prescribed for SPD-
- To strengthen the pelvic floor, back & hip muscles. e.g. strengthening exercises.
- To realizing contracted muscles.e.g. stretching exercises.
- To improve muscle balance & posture g. stabilizing exercises.
- Learning about position & movements that can make the pain worse. Advice on avoiding movements that may be exacerbated the pain.
- A warm bath, an ice pack or heat pack apply to the pubic symphysis or surrounding musculature to reduce pain & muscle spasm & inflammation.
- Exercise in water (hydrotherapy) can help but avoid lots of swimming.
- Postural correction & re-education of body biomechanics.
- Uses crutches, walkers, or other walking aids in severe cases.
- Learning relaxation techniques.
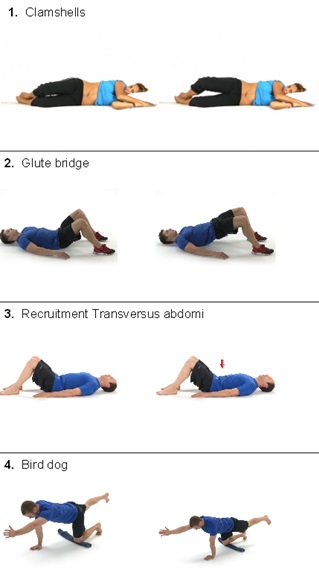
Exercises for SD
There are different types of exercises are recommended for reducing pain, improving stability & correction of abnormality. The success of exercise depends on individual training, use of training daily.
- Strengthening exercises – kegel exercise, pelvic tilt, upper body bending, forward bending exercises are given to the patients to strengthen weak muscles. Exercise has done 10 – 15 minutes/day & 3 – 5 repetitions per exercise & every alternate day is performed for both sides of the body.
- Stretching exercises – stretching of hamstring, adductor groups, quadriceps & side waist muscle. It recommended for reducing muscle spasm. These exercises are performed – 2 times per day & three times per week & 10 – 20 seconds each session.
- Stabilization exercises – it includes strengthening of abdominals, latissimus dorsi, gluteal, pelvic floor & hip adductor muscles. It helps to reduce stress on the joint & improve stability & motor control.
- Aerobic exercise – it includes brisk type walking with medium intensity. It’s performed 25 minutes/day on every alternate day.
- Supine squeeze – patient lies on prone, lying with knees up & feet on the floor. Then the patient will place a pillow between knees & hold a &static squeeze between the buttocks for 30 seconds.
- Deep Abdominal Exercise – it’s performed for increasing core stability & to prevent pelvic or back pain during pregnancy. It started with a few repetitions & gradually increasing. Initially contraction of the transverse abdominals done for the strengthening of deep abdominals.
- Lateral pulls – it’s performed by grasping a door handle & gently pulls it towards himself or
- Kegels’ exercise – patient lie on supine lying, patient gently contracting pelvic floor as if the patient are trying to stop the flow of urine. It helps to strengthen the pelvis & core muscles of the body.
Other therapies
There are some other therapies are recommended for the relief of pain. Such as osteopathy, chiropathy, aromatherapy, acupuncture, hydrotherapy, prolotherapy, and a warm bath.
Symphysis Pubic Dysfunction Support Belt
It uses to manage pelvic joint pain during pregnancy. It significantly reduces sacroiliac joints mobility. It is most beneficial in the later stage of pregnancy. It provides an external force that stabilizes & reduce pressure on the pelvic joints & reducing pain. It also helps to align pelvic bones. It stabilizing tension by dual tension system. This belt must be positioned just cranial to the greater trochanters. It is designed to be flexible to a range of body shapes. It is not recommended for long-term uses due to the weakening of the core muscles.
Home Remedies for SPD
There are some home remedies that reduce pubic symphysis dysfunction related symptoms.
- During sleeping, a pillow placed in between the legs.
- Avoiding prolonged sitting – try not to sit for more than 30 minutes at a time.
- Applying an ice pack or ice cube to the pelvic region.
- Keeping active but avoiding strenuous activity that causes pain.
- Wearing a support belt around the waist.
- Regular doing kegel exercise to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
- Get out of the car without opening legs.
- Getting a massage.
- Roll or slide out of bed without opening legs.
- Using a lumbar cushion for support while riding in the car.
- Wearing farm supportive shoes.
- Incorporating rest breaks every day.
Treating Symphysis Pubic Dysfunction During Pregnancy
There are following steps that help to ease discomfort –
- NSAID is not recommended during pregnancy period.
- Physical therapy – it includes strengthening & stabilization exercise of core muscles for improving pelvic girdle support, soft tissue mobilization techniques or massage, pelvic floor muscle strengthening program, postural exercise & education on body mechanics, taken strategies to minimize pain with activities of daily living.
- Regularly use an ice pack to the pubic symphysis, may help to reduce pain & inflammation. It can be used for 5 minutes at a time or use ice cube for 20 – 30 seconds on pubic symphysis.
- Heating surrounding musculature structure of pelvis may reduce muscle spasm & tightness to decrease pain.
- Kegels & pelvic tilts exercise done regularly. It helps to strengthen the pelvis muscles.
- Specially designed brace or rigid/non-rigid support belt use which can help to the relief of pain. It may help to provide additional stability & decreasing pain with activity.
- Sit down to get dressed & undressed.
- Side-lying can be helpful as long as the abdomen & upper leg are well supported by pillows.
- Try to avoid the stairs.
- Sleep in a comfortable position.
- Keeping active as much as possible within pain limits.
- Rest as much as possible.
- During the night, the use of a pillow between legs may help to support pelvic joints.
- Walk of the stairs one steps at a time
Positions to avoid – during pregnancy, prone lying is not comfortable. After 16 weeks of gestation, supine lying is not advised. Consider alternative positions if wanting sexual intercourse.
Treatment of Symphysis Pubic Dysfunction After Pregnancy
- Different types of electrotherapy modalities can be used for reducing pain. e.g. TENS.
- Mild to moderate types of strengthening exercises are prescribed.
- Activate transversus abdominis by drawing tummy
- Pelvis stabilizer exercise, core muscles exercise.
- Exercises perform 30 minutes per day, 5 – 10 repetitions per exercise, 3 days per week for 7- 10 weeks.
- Adopt a good posture.
- Hydrotherapy – Water aerobics can be a help to reduce pain.
- Soft tissue therapy: it usually includes chiropractic care. It involves spinal manipulation & massage which improve pelvic joint stability & positioning.
- Swimming can be a help to reduce pain & reeducate muscle balance. Breaststroke with legs kicking must be avoided.
- Keeping active as much as possible within pain limits.
- Kinesiotaping techniques also help the patient by the support of the pelvic bones.
- Rest more frequently in a position that is comfortable.
- Avoid bending & twisting movements.
- Avoid straddling & squatting movements.
- Keep core muscles strong by performing by different types of core strengthening exercises.
Symphysis Pubic Dysfunction Surgery
It can be an option for a torn pubic symphysis in severe cases. It is a last case option. It can be also an option for the correction of biomechanical abnormalities (leg length discrepancy, overpronation). In most cases, surgery is avoided unless absolutely necessary. There are following surgery are usually done for SPD –
- Closed reduction with the application of the binder.
- Application of anterior external fixator with or without sacroiliac fixation.
- Anterior internal fixation with plate & screws.
Outlook of Symphysis Pubic Dysfunction
In the case of pregnancy with public symphysis dysfunction, symptoms often reduce a couple of weeks after giving birth. SPD does not directly affect the baby, but it may lead to a more hard pregnancy. Some women may also face vaginal delivery difficulty. Complete resolution may need 9 – 12 months.
Prevention of Symphysis Pubic Dysfunction
There is no specific way to prevent pubic symphysis dysfunction. But a patient can reduce their risk of developing this condition by following below methods –
- Remain active
- Correct positioning
(a) Transitional movements – keeping knees together.
(b) Take smaller steps during walking.
(c) sleeping – put a pillow in between legs & lying on the less painful side.
- Avoid trauma to the pubic symphysis.
- Performing regular pelvic floor exercises.
- Adopt a good posture.
- Wear flat & supportive shoes.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects.
- Changing position frequently.
- During standing to put equal weight on each leg.
- Swimming
- Sit down for a task where possible.
- Use a supportive belt or brace the lower abdominal muscles before performing any activities.
- Regularly done stretch following activity.
Frequently Ask Questions on Symphysis Pubic Dysfunction
What does pubic symphysis dysfunction feel like?
Pain can be felt from being a dull ache to stabbing, sharp, shooting burning, or tearing sensation.
How long does symphysis pubic dysfunction last?
Generally, symptoms of SPD are improved after giving birth. When the relaxin hormone is not produced, the joints become more stable & improve the comfortable label.
How can I strengthen my symphysis pubic?
Pubic symphysis can be strengthened by spinal, abdominals, pelvic floor, pelvic girdle & hip muscle strengthening exercises.
How do you sleep with pubic symphysis dysfunction?
Lying on the less painful side while sleeping. Lie on a painless side with a pillow between legs. Using a pillow under pregnancy women bump & between legs for additional support in bed. When turning over, keep knees together where possible & contract core abdominal muscles.
Why does SPD get worse at night?
SPD gets worse at night when a patient lying on their back. The pelvis is in an unlocked or less stable position which causes pain.
How do you give birth to SPD?
Hands & knees position is most helpful for most women with SPD. In the case of pregnancy with SPD, it is difficult to open her legs. Your doctor will choose the epidural to make the entire process as comfortable as possible. In severe cases where painful movement is present, a doctor may offer a cesarean section.
Does SPD cause more painful labor?
Ideally, SPD should not affect labor in any way. Some pregnant women may have difficulty in vaginal delivery.
